This topic only applies to Intel® 64 architecture targeting the Intel® Xeon Phi™ coprocessor x100 product family (formerly code name Knights Corner).
These class libraries include:
-
Integer vector classes
-
Floating-point vector classes
You can find the definitions for these classes in the header file: micvec.h.
Details About the Class Libraries
These class libraries for SIMD operations provide a convenient interface to access the underlying instructions for processors as specified in Processor Requirements for Use of Class Libraries. These processor-instruction extensions enable parallel processing using the single instruction-multiple data (SIMD) technique as illustrated in the following figure:
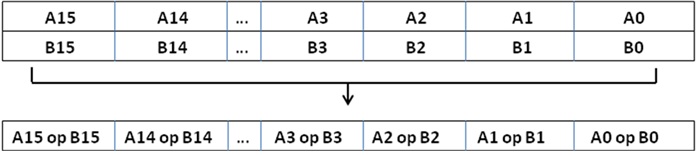
Performing sixteen operations with a single instruction improves efficiency by a factor of sixteen for that particular instruction.
These new processor instructions can be accessed using assembly inlining, intrinsics or SIMD classes for Intel® 64 architecture targeting the Intel® Xeon Phi™ coprocessor x100 product family (formerly code name Knights Corner). Compare the coding required to add sixteen 32-bit floating-point values, using each of the available interfaces:
The following table shows an addition of two single-precision floating-point values using assembly inlining, intrinsics, and the libraries.
| Assembly Inlining | Intrinsics | SIMD Class Libraries |
|---|---|---|
__m512 a,b,c;
__asm {
vmovaps zmm0,b
vmovaps zmm1,c
vaddps zmm0,zmm0,zmm1
vmovaps a,zmm0
}
|
#include <immintrin.h> ... __m512 a,b,c; a = _mm512_add_ps(b,c); ... |
#include <micvec.h> ... F32vec16 a,b,c; a = b + c; ... |