Given a set X of n feature vectors x 1= (x 11,…,x 1p ), ..., x n = (x n1,…,x np ) of dimension p, the problem is to identify the vectors that do not belong to the underlying distribution (see [Ben05] for exact definitions of an outlier).
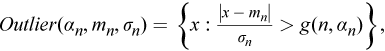
where m n and σ n are (robust) estimates of the mean and standard deviation computed for a given data set, α n is the confidence coefficient, and g (n, α n ) defines the limits of the region and should be adjusted to the number of observations.