When large amounts of data are sent across devices or need to be stored in memory or in a persistent storage, data compression enables you to reduce network traffic, memory, and persistent storage footprint. Intel DAAL implements several most popular generic compression and decompression methods, which include ZLIB, LZO, RLE, and BZIP2.
General API for Data Compression and Decompression
The
CompressionStream and
DecompressionStream classes provide general methods
for data compression and decompression. The following diagram illustrates the
compression and decompression flow at a high level: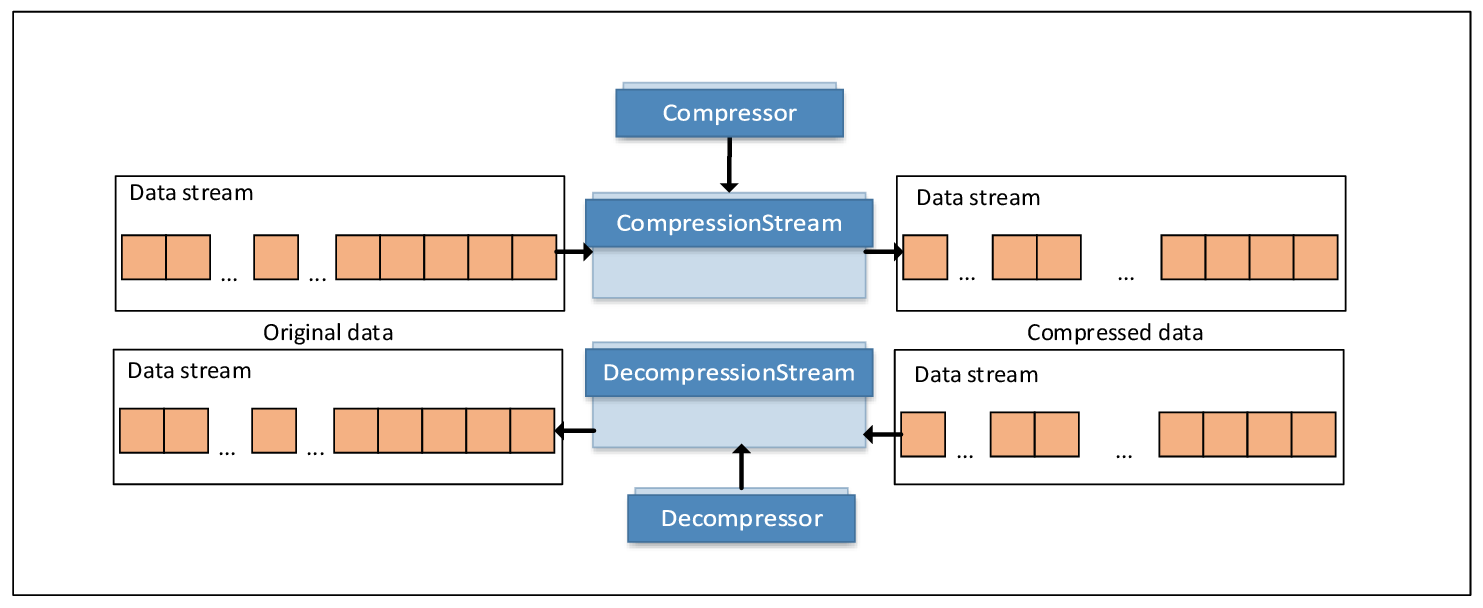
To define compression or decompression methods and related parameters, provide Compressor or Decompressor objects as arguments to CompressionStream or DecompressionStream constructors respectively. For more details on Compressor and Decompressor, refer to Compression and Decompression Interfaces.
Use operator << of CompressionStream or DecompressionStream to provide input data for compression or decompression stream. By default, all compression and decompression stream methods allocate the memory required to store results of compression and decompression. For details of controlling memory allocation, refer to Compression and Decompression Interfaces.
The following methods are available to retrieve compressed data stored in CompressionStream:
-
Copy compressed data blocks into a contiguous array using the copyCompressedArray() method.
You can define the data blocks to copy by specifying the number of bytes to copy. The method copies the data from the beginning of the stream and removes the copied data from CompressionStream, so next time you call the copyCompressedArray() method, it copies the next block of data. To copy all the data, before a call to copyCompressedArray(), call the getCompressedBlocksSize() method to get the total size of compressed data in the stream.
-
Call the getCompressedBlocksCollection() method.
Unlike the copyCompressedArray() method, getCompressedBlocksCollection() does not copy compressed blocks but provides a reference to the collection of compressed data blocks. The collection is available until you call the getCompressedBlocksCollection() method next time.
The following methods are available to retrieve decompressed data stored in DecompressionStream:
-
Copy decompressed data blocks into a contiguous array using the copyDecompressedArray() method.
You can define the data blocks to copy by specifying the number of bytes to copy. The method copies the data from the beginning of the stream and removes the copied data from DecompressionStream, so next time you call the copyDecompressedArray() method, it copies the next block of data. To copy all the data, before a call to copyDecompressedArray(), call the getDecompressedBlocksSize() method to get the total size of decompressed data in the stream.
-
Call the getDecompressedBlocksCollection() method.
Unlike the copyDecompressedArray() method, getDecompressedBlocksCollection() does not copy decompressed blocks but provides a reference to the collection of decompressed data blocks. The collection is available until you call the getDecompressedBlocksCollection() method next time.
Compression and Decompression Interfaces
CompressionStream and DecompressionStream classes cover most typical usage scenarios. Therefore, you need to work directly with Compressor and Decompressor objects only in the cases as follows:
-
CompressionStream and DecompressionStream classes do not cover your specific usage model.
-
You want to control memory allocation and deallocation for results of compression and decompression.
-
You need to modify compression and decompression default parameters.
The Compressor and Decompressor classes provide interfaces to supported compression and decompression methods (ZLIB, LZO, RLE, and BZIP2).
Compression and decompression objects are initialized with a set of default parameters. You can modify parameters of a specific compression method by accessing the parameter field of the Compressor or Decompressor object.
To perform compression or decompression using the Compressor or Decompressor classes, respectively, provide input data using the setInputDataBlock() method and call the run() method. This approach requires that you allocate and control the memory to store the results of compression or decompression. In general, it is impossible to accurately estimate the required size of the output data block, and the memory you provide may be insufficient to store results of compression or decompression. However, you can check whether you need to allocate additional memory to continue the run() operation. To do this, use the isOutputDataBlockFull() method. You can also use the getUsedOutputDataBlockSize() method to obtain the size of compressed or decompressed data actually written to the output data block.
You can use your own compression and decompression methods in CompressionStream and DecompressionStream. In this case, you need to override Compressor and Decompressor objects.