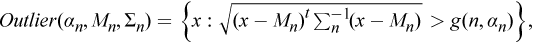Given a set
X of
n feature vectors
x
1=
(x
11,…,x
1p
),
...,
x
n
=
(x
n1,…,x
np
)
of dimension
p, the problem is to identify the vectors that do not
belong to the underlying distribution (see [Ben05]
for exact definitions of an outlier).
The multivariate
outlier detection method takes into account dependencies between features. This
method can be parametric, assumes a known underlying distribution for the data
set, and defines an outlier region such that if an observation belongs to the
region, it is marked as an outlier. Definition of the outlier region is
connected to the assumed underlying data distribution. The following is an
example of an outlier region for multivariate outlier detection:
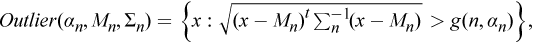
where
M
n
and
Σ
n
are
(robust) estimates of the vector of means and variance-covariance matrix
computed for a given data set,
α
n
is the
confidence coefficient, and
g (n,
α
n
)
defines the limit of the region.