To access this window: Select the Platform Power Analysis viewpoint and click the Temperature sub-tab in the result tab.
Use the Temperature window to:
- Identify how much time each core spent in each temperature.
- Review the systems on a core (SOC) temperature samples (Intel® Atom™ cores only).
Note
Platform Power Analysis viewpoint is available as part of Energy analysis. Energy analysis with the Intel® SoC Watch data collector is available for target Android*, Windows*, or Linux* devices and provided only with the Intel® VTune™ Amplifier for Systems.
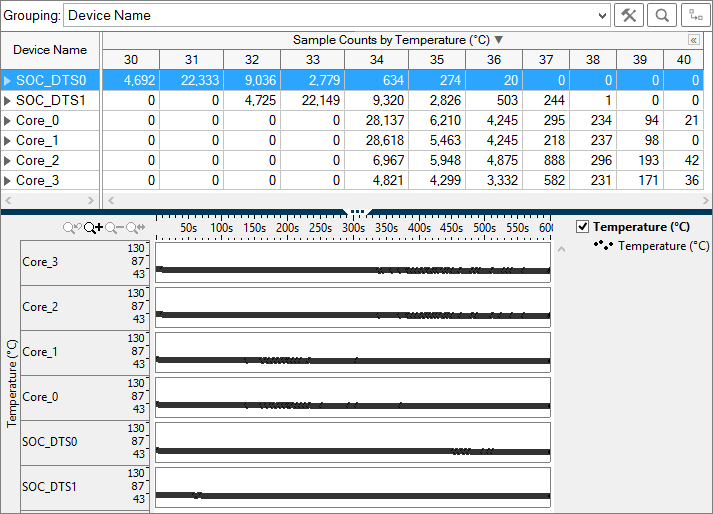
Temperature Pane
The Temperature pane shows the sample counts at each temperature
reading in degrees Celsius (oC) for each core or device. A greater
number of sample counts indicates that the device or core spent more of the
collection time at that temperature. Click the expand![]() /collapse
/collapse![]() buttons in the data columns to
expand the column and show data for different temperature readings in each
device. You can change the unit displayed by right-clicking a data cell and
selecting the
Show Data As option to select an alternate unit. For example,
you can display the sample counts as a percentage of the total sample counts.
buttons in the data columns to
expand the column and show data for different temperature readings in each
device. You can change the unit displayed by right-clicking a data cell and
selecting the
Show Data As option to select an alternate unit. For example,
you can display the sample counts as a percentage of the total sample counts.
Timeline Pane
The Timeline pane displays the temperatures of each core at each point in time during the collection. Expand the timeline rows vertically to view subtle temperature shifts. Zoom in on the timeline to view sampling points. Filters applied on a timeline in one window are applied on all other windows within the viewpoint. This is useful if you identify an issue on one tab and want to see how the issue impacts the metrics shown on a different tab.
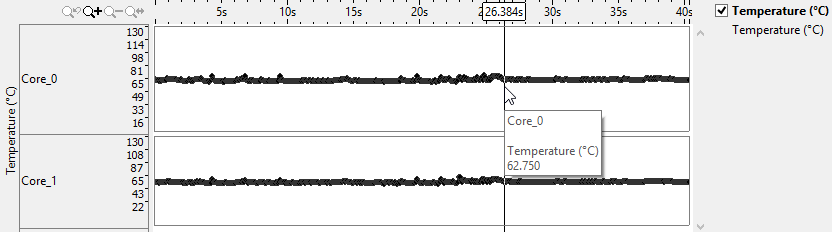
Shifts in core temperature often mirror shifts in processor frequency. When the processor runs at a higher frequency, the temperature also rises. In the following example, the temperature fluctuates for the first 26 seconds of collection and then remains fairly stable.
The same stabilization trend is observed in the frequency timeline on the CPU C/P States window for the same collection.
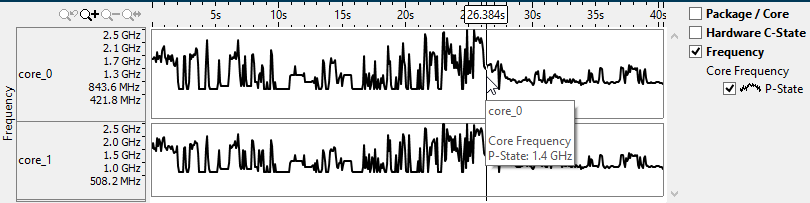
If the temperature is high, but the frequency is low, it could mean that the CPU is being throttled to lower core temperature.