To access this window in the Refinement Reports, double-click a data row or use the corresponding context menu item to view the source code associated with a Problem, Message, or Code Location.
Use this window to examine the source code for a selected Problem, Message, or Code Location. To modify your source code, double-click a source line or use the Edit Source context menu item to display that file in a code editor.When using the Intel Advisor GUI, the editor defined by the Options > Editor dialog box appears with the file open at the corresponding location.
|
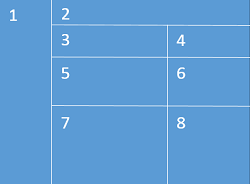
Dependencies Source Window Layout
|
|
Use This |
To Do This |
|---|---|
|
Run a tool of your choice and see results in the Result tab. |
|
|
Select between available reports. |
|
|
Focus Code Location pane |
Explore the source code associated with the focus code location. |
|
Select the source code to appear in the Focus Code Location pane. |
|
|
Explore source code associated with the code locations. This pane does not appear if the Focus Code Location does not have a Related Code Location. |
|
|
Select the source code to appear in the Related Code Location pane. This pane does not appear if the Focus Code Location does not have a Related Code Location. |
|
|
Code Locations pane |
View details about the code locations for the selected problem in the Dependencies Source window. |
|
Relationship Diagram pane |
View the relationships among code locations for the selected problem. |
Using Dependencies Data
Use the Dependencies Report to view each reported problem and its associated code locations. Use the Dependencies Source window to view the focus and related source code regions to help you understand the cause of the reported problem.
To learn about a reported problem, do one of the following:
-
Right-click its name in the Dependencies Report, Problems and Messages pane and select What Should I Do Next?. This displays the help topic for that problem type.
-
View About Problems and Message Types and click the link for the reported problem. This displays the help topic for that problem type.