To access this window: Select the Platform Power Analysis viewpoint and click the Core Wake-ups sub-tab in the result tab.
Use the Core Wake-ups window to:
- Identify wake-up reasons on each core.
- Investigate wake-up reasons at a specific time during the collection.
- Sort data based on wake-up reason to identify common causes.
- View the objects that caused wake-ups.
Note
Platform Power Analysis viewpoint is available as part of Energy analysis. Energy analysis with the Intel® SoC Watch data collector is available for target Android*, Windows*, or Linux* devices and provided only with the Intel® VTune™ Amplifier for Systems.
Core Wake-ups Pane
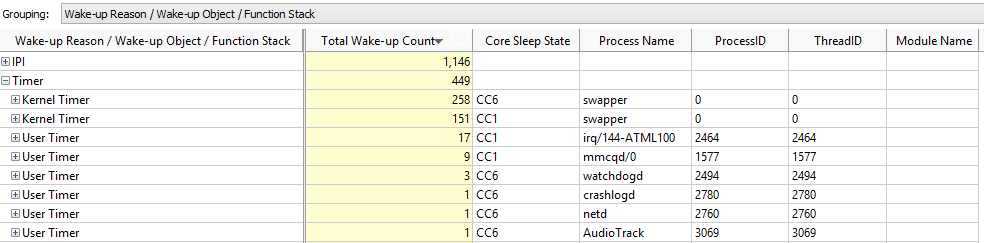
The Core Wake-ups pane displays information about events that caused the core to switch from a sleep state to an active state. This data is only collected when C-States data is collected. Display the information grouped by core or package, wake-up reason, wake-up object, and function stack using the Grouping drop-down. By default, the table is sorted by the Total Wake-up Count metric in the descending order providing objects with the highest wake-up count first.
A core is active when the core sleep state is C0 and is inactive, or sleeping, when the sleep state is Cn, where the higher the n value, the deeper the sleep state. The sleep states are displayed with a different prefix for package (PCn), module (MCn), or core (CCn). In the example below, the first Kernel Timer has a Core Sleep State value of CC6, which means the core was in the deepest sleep state.
Note
Additional details about the wake-up objects, such as Process Name or ThreadID, are available for results collected on a Linux* or Android* system only.
Wake-up Reason |
Description |
|---|---|
CLK |
Clock interrupt |
DPC |
Deferred procedure call |
INT |
Hardware interrupt |
IPI |
Inter-processor interrupt |
IRQ |
Interrupt request (Android*) |
RDY |
Ready event |
Scheduler |
Scheduler event |
Timer |
Timer event |
Unknown |
The operating system did not log a wake-up reason between exiting idle and re-entering idle or the wake-up reason was not passed to Intel VTune Amplifier. |
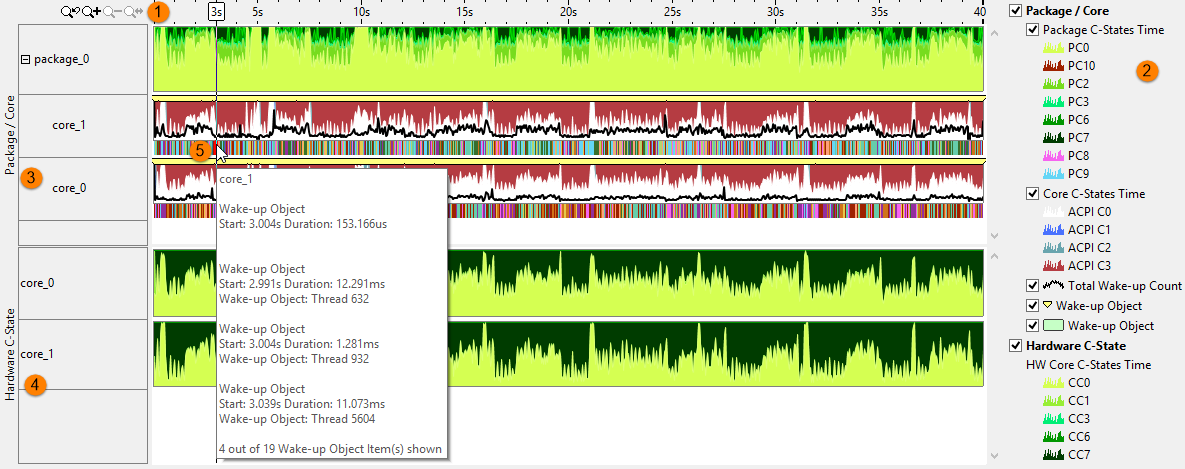
Timeline Pane
The Timeline pane shows the time spent in the active state (C0) or the various sleep states (Cn) as well as the total wake-up count for the package, package cores, and hardware cores. Use the Core Wake-ups pane to filter the wake-up types shown in the timeline by right-clicking a wake-up reason and selecting Filter In by Selection. Filters applied on a timeline in one window are applied on all other windows within the viewpoint. This is useful if you identify an issue on one tab and want to see how the issue impacts the metrics shown on a different tab.
 |
Toolbar | Navigation control to zoom in/out on the view on areas of interest. For more details on the Timeline control, see Managing Timeline View. |
 |
Legend | Types of data presented on the timeline. Filter in/out any type of data presented on the timeline by selecting/deselecting corresponding check boxes. For example, each state is a different color and you may only be interested in the time spent in the active state. You can also filter in and out the hardware or package/core data. The Wake-up Object marker shows processor wake-ups on the timeline. Hover over a yellow marker to see the time when the sleep state changed to an active state and the name of the wake-up object. Zoom in on the timeline to view individual markers if they are not visible when viewing the timeline for the full collection time. |
 |
Package/Module/Core C-states | Graphical representation of the sleep states in each core
and in the overall package. Each state is a different color, which can be
filtered using the legend. Hover over the band to view the total wake-up count.
Click the
|
 |
Hardware C-states | Graphical representation of the sleep states on the hardware. Each state is a different color, which can be filtered using the legend. |
 |
Wake up Band | Represents the wake-up objects that caused the core to switch from a sleep state to an active state. Each wake-up object type uses a unique color. By hovering over the band, you can view all of the wake-up objects at that point in time, including details such as wake-up object type, start time, and duration. Find an area of interest in the timeline, such as a time when the core was active for a period of time, and then select the Zoom In and Filter In by Selection action to view the reasons the core became active. You can view the wake-up reasons and additional details for the time selected in the Core Wake-ups pane. 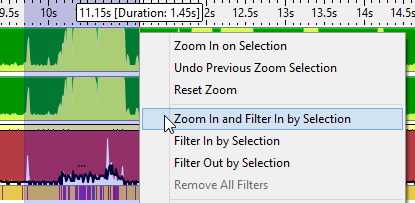 |
 /
/ to expand the package and view
the individual modules and cores.
to expand the package and view
the individual modules and cores.